BLOG
Best Guide to Power Over Ethernet
Table of contents

Introduction to Power Over Ethernet
What is Power Over Ethernet
Power over Ethernet (PoE) is a technology that allows electrical power and data to be transmitted over 100 meters of a single Ethernet cable. This simplifies the installation of network devices, such as IP cameras, wireless access points, POS terminals, kiosks, and VoIP phones, by eliminating the need for separate power supplies. PoE is governed by the IEEE802.3xx standard that defines the methods and specifications for delivering power and data safely and efficiently over Ethernet cables.
Overview of PoE Standards
PoE standards are a set of protocols defined by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) that promotes the development and application of electrotechnology. Regarding PoE, there are three standards; IEEE802.3af, IEEE802.3at, and IEEE802.3bt, which specify power levels, wiring configurations, and other technical parameters to ensure the safe and efficient delivery of power over Ethernet cables. Adherence to PoE standards guarantees compatibility and reliability across different network devices and manufacturers, promoting widespread adoption and interoperability.
IEEE 802.3af (PoE)
The history of Power over Ethernet (PoE) standards began in 2003 with the introduction of IEEE802.3af standard. The IEEE 802.3af standard, also known as the PoE standard, specifies how to safely deliver 15.4W of power from Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE) and 12.95 watts of power at the Powered Device (PD) using 44-57 volts of DC power over Cat5 ethernet cables. The first application was VoIP (Voice Over IP), with other applications, such as WAP (Wireless Access Points), and low-power surveillance cameras quickly adopting the standard, which ensures interoperability between different vendors’ equipment, providing a reliable and widely adopted method for powering network devices.
IEEE 802.3at (PoE+)
In 2009, the IEEE802.3at standard, also known as PoE+, was released. This standard is an enhancement of the IEEE 802.3af standard, providing up to 30 watts from the PSE and 25.5 watts at the PD over Cat5 cables. This higher power level supports more demanding devices like PTZ cameras, higher speed wireless access points and video IP phones. IEEE 802.3at ensures backward compatibility with 802.3af devices while offering increased power for newer, more power-hungry network devices.
IEEE 802.3bt (PoE++)
To meet the growing demand for higher power devices, the IEEE 802.3bt standard was introduced in 2018. Also known as Hi Power PoE (Hi-PoE) and PoE++, the IEEE 802.3bt standard is the latest PoE standard delivering from 60 watts to 90 watts of power from a PSE. The IEEE802.3bt standard is backwards compatible to the IEEE802,3af and IEEE802.3at standards and can support PD’s with power requirements from 51 watts to 71.3 watts. This standard supports high-power devices such as digital signage, LED lighting, and high-performance wireless access points. IEEE 802.3bt provides greater flexibility and scalability for modern networks, accommodating the growing demand for power-intensive applications.
PoE Terminology
In the realm of Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology, several key terms are crucial. This section explores various types of terminology, helping you understand how PoE functions and interacts within network environments.
PSE
Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE) refers to devices that provide power to PoE-enabled devices over Ethernet cables. PSEs can be network switches or PoE midspan/injectors. These devices are responsible for detecting PoE-compatible devices and supplying the appropriate amount of power. PSE plays a critical role in PoE networks, ensuring reliable power delivery and enabling the use of various PoE devices.
PoE Injector and Midspans
PoE injectors and PoE midspans are two terms for the same thing, whether they are 1 port or multi ports. PoE injectors/midspans essentially serve the fundamental purpose of enabling non-PoE network switches to deliver power alongside data to a PoE-compatible device through a single Ethernet cable.
Passive and Active Injectors (Dumb and Smart Injectors)
Passive and Active Injectors are also referred to as Dumb and Smart Injectors: PoE injectors are available in either “passive” or “active” format. Passive PoE injectors provide a fixed output voltage that does not have any negotiation or handshake with the end powered device (PD). Passive Injectors have a simpler design with a lower cost, and are often used in applications where the passive PoE injector and PD are provided together as a bundled solution.
In contrast, active PoE injectors adhere to IEEE standards (such as 802.3af, 802.3at, and 802.3bt) and require a handshake between the active PoE injector and the PD to negotiate and deliver the correct amount of power. The handshake between the active PoE injector and PD is crucial to ensure powering compatibility to avoid damage to the PD. This ensures safety, compatibility, and adaptability to a variety of devices, making active PoE Injectors the perfect solution for open architecture systems requiring the interoperability between injector and PD’s from different manufacturers.
Detection
Detection in Power over Ethernet (PoE) refers to the process by which Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE) identifies whether a connected device is PoE-compatible and capable of receiving power. This detection mechanism is essential to prevent accidental damage to non-PoE devices and ensures efficient power delivery to PoE-enabled devices. Typically, detection involves the PSE sending a low voltage signal down the Ethernet cable to check for the presence of a valid PoE signature. If the connected device responds appropriately, indicating it can accept PoE, the PSE then proceeds to deliver power at the appropriate voltage and current levels. This detection process is standardized across different PoE implementations (such as IEEE 802.3af, 802.3at, and 802.3bt), ensuring compatibility and safe operation within PoE networks.
Classification
Classification in Power over Ethernet (PoE) refers to the process by which Powered Devices (PDs) are categorized based on their power requirements. This classification helps Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE) determine how much power to deliver. PDs can be classified into different classes (such as Class 0 to Class 4), each corresponding to specific power needs defined by IEEE standards (802.3af, 802.3at, 802.3bt). Higher classes require more power, accommodating devices with greater power demands like PTZ cameras with heaters or wireless access points. Understanding classification is crucial for ensuring proper power allocation in PoE networks and avoiding overloading or underpowering devices, thereby optimizing network performance and reliability.
Disconnect
In Power over Ethernet (PoE) terminology, “disconnect” refers to the mechanism that ensures safe power delivery in case of faults or when devices are unplugged. This feature is crucial for protecting both the equipment and the network from potential damage due to unexpected power surges or short circuits. After power is applied to a PD the load is constantly monitored to ensure that it stays within specified envelopes of current, voltage and time. When a disconnect event occurs, the PSE detects an out of envelope level and ceases power delivery to the affected port or device, preventing any potential harm. Understanding disconnect mechanisms is essential for maintaining the reliability and safety of PoE networks, ensuring uninterrupted operation and protection against electrical hazards.
PD
In Power over Ethernet (PoE) terminology, “PD” stands for Powered Device. PDs are devices that receive power and data through Ethernet cables from Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE) such as PoE switches or injectors. These devices include IP cameras, wireless access points, VoIP phones, and other network devices designed to operate with PoE technology. PDs are classified into different categories (Class 0 to Class 4) based on their power consumption needs, allowing PSEs to deliver the appropriate amount of power efficiently. Understanding PDs is essential for designing, deploying, and managing PoE networks effectively, ensuring seamless integration and reliable operation of powered devices.
Traditional Data Network vs. POE Data Network
Traditional data networks and Power over Ethernet (PoE) data networks differ primarily in their ability to deliver power alongside data over Ethernet cables. In traditional data networks, Ethernet cables are solely used for transmitting data between network devices such as computers, routers, and switches. Power is typically supplied through separate electrical cables or adapters. In contrast, PoE data networks integrate power delivery into the same Ethernet cables used for data transmission. This integration eliminates the need for additional power cables or adapters, simplifying installation and reducing infrastructure costs. PoE technology enables devices like IP cameras, wireless access points, and VoIP phones to receive both power and data from a single network connection, enhancing flexibility and efficiency in network deployments.
Types of PoE Network Components
PoE Injectors
A PoE injector, also known as a midspan, is a device that adds power to an Ethernet cable for PoE-enabled devices. It is used when a network switch does not natively support PoE. The injector connects to the non-PoE switch and the end device, providing the necessary power for devices such as IP cameras and access points. An injector can also supplement PoE switches that cannot provide enough power to all ports. PoE injectors are classified as Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE) and are crucial for extending PoE capabilities to existing network setups.
PoE Splitters
A PoE splitter divides the power and data coming from a single Ethernet cable into separate outputs. Power is usually separated to a barrel jack connector, with the data remaining on a RJ45 connector. This allows a non-PoE capable device to receive power and data from a PSE, greatly simplifying installations where only one cable run is feasible. PoE splitters are often used in conjunction with either a PoE injector or PoE switch, thus making it easier to integrate legacy PDs into PoE networks.
PoE Extenders
A PoE extender is a device used to extend the reach of Power over Ethernet (PoE) beyond the standard distance limitations imposed by Ethernet cables. Ethernet cables are typically limited to a maximum length of 100 meters (328 feet) for both data and power transmission. A PoE extender helps overcome this limitation by amplifying and forwarding both the data and power signals, allowing network devices to be placed further away from the power source.
PoE Media Converter
A PoE media converter is a device that bridges different types of network media while also providing Power over Ethernet (PoE) capabilities. It converts one type of network connection (such as fiber optic) to another type (such as twisted-pair Ethernet), and simultaneously delivers power over the Ethernet cable to PoE-enabled devices. Fiber cables allow longer runs than traditional copper cables do so this combination of media conversion and PoE functionality makes PoE media converters versatile and useful in various long distance networking scenarios.
PoE-to-USB Converter
A PoE-to-USB converter is a device that converts power and data through an Ethernet cable to a USB output, allowing USB-powered devices to be powered through an Ethernet cable. This is particularly useful for deploying USB devices like tablets, smartphones, webcams, or IoT gadgets in locations where traditional power sources are unavailable or inconvenient. By leveraging PoE infrastructure, these converters simplify installations and reduce the need for additional wiring.
9 Key Features & Benefits of PoE Injectors:
Power and Data Over One Cable: Simplifies installation and reduces clutter.
Flexibility: Supports devices in locations without power outlets.
Cost Efficiency: Reduces the need for additional wiring and electrical work.
Scalability: Easily expand networks by adding more PoE devices.
Safety: Built-in protection features and safe power delivery.
Remote Management: Allows for monitoring and control of devices remotely.
Compatibility: Works with a wide range of devices like cameras, phones, and access points.
Easy Installation: Plug-and-play setup for quick deployment.
The Ultimate Guide to PoE Extenders: Overcoming Limitations
FAQ
What are the differences between a regular PoE injector and a PoE-to-USB converter?
A PoE injector is going to provide power through an Ethernet cable connected to its RJ45 port to the powered device as well as pass data between the powered device and switch. PoE-to-USB converter is going to take that power and data and utilize USB-C to provide power to charge a device and pass data.
Is a PoE splitter the same thing as a PoE injector?
No. They’re two different things. An injector injects its own power and passes data through the Ethernet cable between the switch and device, whereas a splitter needs power from a PSE, such as the injector, and splits the data and power to a non-PoE device. Depending on the splitter, it could also convert the DC voltage from the PSE to another DC output voltage required of the device to operate.
Can I use your PoE splitter with any brand injector and powered device?
As long as the splitter and injector are standards based, then it should be able to work with any brand.
Do I need a splitter with my POE injector?
Not necessarily. A splitter is only required if the powered device is not standards based.
What are the key differences between IEEE 802.3af, 802.3at, and 802.3bt standards in terms of power delivery and device compatibility?
IEEE 802.3af provides up to 15.4 watts, IEEE 802.3at provides up to 30 watts, and IEEE 802.3bt offers from 60 watts (Type 3) to 90 watts (Type 4) at the PSE. Higher standards support more power-hungry devices while ensuring compatibility and reliability.
Related Articles
PoE Injector Explained: A Complete Overview of Power over Ethernet Technology
Learn how PoE injectors streamline network setups by delivering power and data via one cable. This guide covers benefits, applications, and features of PoE.
Introduction to PoE Injectors: What Are PoE Injectors? A Beginner’s Guide to Power over Ethernet Solutions
This beginner’s guide introduces PoE injectors, explaining what they are and how they enhance Power over Ethernet solutions by providing power to network devices without requiring additional outlets.
802.3af, at and bt: Exploring Active Power Over Ethernet IEEE Standards
Explore PoE standards including IEEE 802.3 af, 802.3 at, 802.3 bt, and more. Learn how these standards revolutionize Power over Ethernet networks.
PoE Glossary: Demystifying Power over Ethernet Terminology, a Comprehensive Guide
Explore the PoE Glossary for clear definitions of Power over Ethernet terms. Enhance your understanding of networking technology effortlessly.
PoE Network vs Traditional Data Networks: The Differences and Benefits
Explore the differences and benefits of a PoE network versus traditional data networks in this insightful comparison.
PoE Components: A Detailed Overview of Various Network Component Types
This article dives into various network and PoE components, explaining their roles and how they integrate within a PoE-enabled network.
Top PoE Components: Exploring Key PoE Network Device Types
Discover the essential PoE components in this article, exploring key network device types that enhance Power over Ethernet systems and improve connectivity and efficiency.
Phihong and the History of PoE: Tracing the Evolution of Power over Ethernet Technology
Explore Phihong’s pivotal role in the evolution of Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology, highlighting key milestones that transformed network power delivery and device connectivity.
Understanding the IEEE 802.3af Standard: Basics of Power over Ethernet (PoE)
Explore the IEEE 802.3af standard in this article, which outlines the basics of Power over Ethernet (PoE) and its role in efficient power delivery to network devices.
Understanding the IEEE 802.3at Standard: Advanced Power over Ethernet (PoE) Explained
Dive into the IEEE 802.3at standard in this article, which explains advanced Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology and its enhanced capabilities for delivering power to network devices.
Exploring the IEEE 802.3bt Standard: Unlocking the Power of PoE++ Technology
Discover the IEEE 802.3bt standard in this article, which unlocks the potential of PoE++ technology for delivering higher power levels to network devices, enabling advanced applications and improved efficiency.
Power Over Ethernet: De-tangling the Mystery of PoE Injectors
This article clarifies the role of PoE injectors in Power over Ethernet systems, explaining their function, benefits, and how they simplify network setup by eliminating the need for separate power cables.
OUR MISSION
"Phihong USA delivers reliable, innovative power solutions, enhancing efficiency and sustainability. We focus on advancing technology in power supplies, PoE solutions, and EV charging systems to meet diverse industry needs globally."
Benefits of Active Power Over Ethernet
Safety and Performance
Power over Ethernet (PoE) significantly enhances electrical safety by operating at a low voltage (typically 56V DC), reducing the risk of electric shock during installation and maintenance. Compliance with IEEE802.3 standards ensures that PoE systems safely manage power delivery, preventing overloading or underpowering of devices. Centralized power management and built-in safety features further contribute to a secure operational environment, offering protection against electrical hazards and ensuring reliable device performance.
Enhanced Electrical Safety
PoE operates at a low voltage (typically 56V DC), significantly reducing the risk of electric shock compared to standard mains voltages (110V or 220V AC). This makes installation and maintenance safer, even without specialized electrical training.
Compliance with IEEE802.3 Standards
To ensure a safe PoE network, IEEE802.3 standards-based Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE) and Powered Devices (PD) are crucial. Standards-compliant PSEs detect the impedance of PDs before supplying power, ensuring proper power delivery without overloading or underpowering devices.


Centralized Power Management
PoE enables centralized control over power, allowing administrators to remotely manage device power status. This capability can facilitate energy savings by shutting down devices when not needed.
Built-in Safety Features
Many PoE systems incorporate essential safety mechanisms such as overload, short circuit, and overvoltage protection. These features prevent device damage and reduce the risk of fire or electrical hazards, ensuring reliable and safe operation.
Device Protection and Isolation
PoE injectors and switches often provide electrical isolation between the power source and devices. This isolation protects against electrical faults, further enhancing the safety and longevity of connected equipment.
Reliability
Reliability of PoE lies in its streamlined infrastructure, centralized power management, and built-in protective features and adaptability. All of which contribute to a stable and dependable network environment.
Surge Protection
Some PoE systems include built-in surge protection and power management features that safeguard connected devices against electrical surges and spikes. This protection extends the lifespan of devices and maintains reliable operation.
Cost Savings
With PoE, both power and data are delivered through a single Ethernet cable, eliminating the need for an electrician or separate electrical wiring and outlets. This reduces labor costs and installation time. Additionally, PoE is scalable and enables flexible device placement, enhancing network coverage without expensive infrastructure changes. Overall, it offers significant cost savings and optimizes network infrastructure economically.
No Conduit for Power Cables
Not having the need for separate pathways for power cables means not only does Power over Ethernet simplify installation, but it reduces costs, allowing more flexible placement of devices.
Elimination of Electrical Infrastructure
PoE-powered devices do not require proximity to electrical outlets. This flexibility in device placement can lead to cost savings, especially in areas where installing new electrical outlets would be difficult or expensive. Installing electrical wiring typically requires a licensed electrician, which can be costly. PoE installations can often be completed by network technicians, who generally charge less than electricians. Avoiding the need for additional electrical circuits and outlets reduces the overall cost of electrical infrastructure.
Lower Maintenance and Management Costs
PoE allows for centralized power management, making it easier to monitor and control power consumption. This can lead to operational efficiencies and cost savings in managing the power needs of various devices.
Enhanced Flexibility and Scalability
Adding or relocating PoE devices is simpler and less costly because it often involves just plugging in an Ethernet cable without worrying about power sources. This flexibility can lead to cost savings in future expansions or reconfigurations.
Standards Based Interoperability
Standards Compliance
PoE injectors that comply with IEEE standards (such as 802.3af, 802.3at, and 802.3bt) ensure compatibility with a wide range of devices, from IP cameras to wireless access points.
Interoperability
They work seamlessly with other network equipment, allowing for a cohesive network environment.
Simplifying Installation
Reduced Cabling Requirements
PoE combines power and data transmission over a single Ethernet cable, eliminating the need for separate power and data cabling. This reduces the amount of cabling required and simplifies the installation process.
Simplified Installation
With PoE, devices can be installed without the need of an electrician. This simplifies the work for installers and reduces labor costs. With fewer cables and a more straightforward network design, troubleshooting and maintenance are easier and less time-consuming, reducing ongoing maintenance costs.
Improved Aesthetics
Fewer cables lead to a cleaner installation, reducing clutter and potential tripping hazards. This can indirectly save costs related to workplace safety and aesthetics.
14 Key Advantages of Using PoE Injectors
Superior electrical safety
Compliance standards for active PoE (IEEE802.3)
Centralized power management
Built-in safety features
Device protection and isolation
Surge Protection
No Conduit needed
Devices don’t require localized power outlet
Lower maintenance and management costs
Enhanced flexibility and scalability
Interoperability
Reduced cabling requirements
Simplified installation
Improved aesthetics
FAQ
How does active PoE enhance safety and performance in network systems?
Active PoE automatically detects and delivers the precise power required, ensuring optimal performance and preventing damage to devices, thereby enhancing overall network safety.
Why is active PoE considered more reliable than passive PoE?
Active PoE systems continually monitor and adjust power levels, providing consistent and reliable power delivery that minimizes the risk of overloading or underpowering devices.
How does active PoE contribute to cost savings in network installations?
By eliminating the need for separate power cables and outlets, active PoE reduces installation and maintenance costs, leading to significant long-term savings.
What is the advantage of PoE’s standards-based interoperability?
Standards-based PoE ensures compatibility between devices from different manufacturers, allowing for flexible and scalable network deployments without compatibility issues.
How does PoE simplify network installation?
PoE simplifies installation by enabling both power and data to be delivered over a single Ethernet cable, reducing the complexity and time required for setup.
Related Articles
PoE Injectors: Unlocking the Advantages of Active Power over Ethernet (PoE)
Explore the advantages of Active PoE systems, focusing on safety, performance, reliability, cost savings, and streamlined installations with PoE injectors.
PoE Applications in Various Industries


Telecom
Voice and Communication
VoIP phones and video conferencing systems are powered and connected via PoE, enhancing office communication. Conference phones and PBX systems also benefit, ensuring clear and reliable communication solutions.
Datacom
Networking
Wireless networks benefit from PoE, with devices like Wireless Access Points (WAPs) providing both data connectivity and power. PoE supports mesh networking devices, extending coverage, and bridges that connect distant segments without additional power sources. WiFi networks, integral to both residential and commercial environments, rely on PoE to power various networking components, ensuring seamless and reliable wireless connectivity. Additionally, 5G technology, which promises faster speeds, lower latency, and higher capacity, can utilize PoE to power small cell installations, enhancing network performance and coverage.
Data Centers
PoE midspans can power non-PoE network infrastructures for networking equipment, servers, and other devices.
Security
Surveillance
PoE technology is integral to security systems, powering IP cameras for surveillance, access control systems (including biometric fingerprint, facial recognition devices, card readers, electronic locks, keypads, etc.), electronic gate locks and intercom systems for seamless communication in buildings.
Retail
Retail (Kiosks, Displays, POS Systems)
Self-checkout and point-of-sale (POS) machines in grocery and retail stores, price-checking kiosks, digital advertising, informational displays, ticket machines, printers, patient check-in kiosks in hospitals, can utilize PoE technology.
Industrial
Lighting
PoE lighting offers significant advantages in industrial environments. By using Ethernet cables to deliver both power and data to LED lighting fixtures, facilities can achieve greater energy efficiency and simplified installation. PoE lighting systems can be integrated with sensors and building management systems, enabling smart lighting controls such as occupancy sensing, daylight harvesting, and remote management. This integration results in reduced energy consumption, lower maintenance costs, and enhanced operational flexibility.
Building Automation
In building automation, PoE powered LED lighting in offices, retail spaces, and warehouses offer energy efficiency and control advantages. Sensor control systems monitor temperature and humidity. Building automation systems communicate with HVAC systems, incorporating features like occupancy sensors and smart thermostats.
Robotics
In robotics, PoE technology powers robotic arms and manipulators for industrial tasks, supports automated guided vehicles (AGVs) in logistics operations, and enables drones and UAVs for surveillance and aerial missions.
Infrastructure & Public Utilities
Outdoor PoE
Outdoor PoE applications are critical in infrastructure and public utilities. These include powering outdoor security cameras, environmental monitoring systems, traffic management systems, and public WiFi hotspots. PoE can also support street lighting and smart city applications, where sensors and communication devices are integrated into municipal services. Using PoE for these applications simplifies installation and maintenance, ensures reliable power delivery in various weather conditions, and enhances the scalability of urban infrastructure projects.
Public Transit
Transportation Mode
Phihong’s Power-over-Ethernet DC input injectors provide a flexible power delivery option for PoE-enabled devices that operate on DC power sources. These injectors enable the transmission of power and data over ethernet cables, facilitating the use of IP security cameras in environments where DC power infrastructure is prevalent. Users can link them to a battery source. Phihong PoE DC input injectors support data speeds of up to 2.5G and are available in 30W and 90W variants. Common applications include trains, locomotives, and transit surveillance systems.
Medical
Hospitals & Care Facilities
Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology is increasingly being applied in the medical industry to enhance efficiency and functionality in various healthcare environments. PoE lighting systems provide reliable and energy-efficient illumination in hospitals and clinics, allowing for centralized control and integration with other smart building systems. In greenfield applications, where new healthcare facilities are being built, PoE infrastructure offers a flexible and scalable solution for deploying advanced medical equipment and devices. Additionally, PoE supports robust Wi-Fi networks essential for seamless communication, telemedicine, and real-time patient monitoring, ensuring that medical staff have access to critical information whenever needed.
PoE Applications: Wattage and Voltage Range Overview
This should be the most obvious feature of all, there are different wattages and voltages for different types of applications. Phihong carries a wide range of products varying power outputs. Wattage ranges from 13W – 576W, and output voltage can range from 5V-56V.
Low power PoE Injector Applications (13W – 30W):
IP Cameras: A low power injector is commonly used to power Internet Protocol (IP) cameras and other surveillance systems like Network Video Recorders (NVRs).
Access Control Systems: PoE injectors can power access control devices such as card readers, keypads, door controllers, biometric fingerprint and facial recognition devices.
VoIP Phones: Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) phones and intercoms often utilize injectors to power individual phones in offices or call centers.
Point-of-Sale (POS) Systems: PoE injectors can power devices such as barcode scanners or card readers in retail environments.
Wireless Bridges: A low power injector would be great for powering a wireless bridge. It’s a networking device that connects two or more separate wired networks or network segments.
Enabling communication between devices on each network as if they were directly connected by a physical cable, even if they’re located far apart and cannot be connected by traditional means.
Medium power PoE Injector & Midspan Applications (45W – 90W):
Small to Medium-Sized Networks: Medium power injector would have no problem powering a variety of devices in small to medium-sized networks and Network Attached Storage (NAS) hubs.
Digital Signs: PoE injectors are commonly used to power large digital displays, media players, and other small to medium-sized LED displays.
Building Automation Systems: PoE injectors can power sensors, actuators, and other building components, enabling centralized control and monitoring of various building functions such as lighting, HVAC, and security.
Monitoring Systems: A medium power option would be a great option for outdoor environmental monitoring systems, remote sensors, and IoT devices deployed outdoors or in harsh, secluded environments.
PoE Applications: Wattage and Voltage Range Overview
This should be the most obvious feature of all, there are different wattages and voltages for different types of applications. Phihong carries a wide range of products varying power outputs. Wattage ranges from 13W – 576W, and output voltage can range from 5V-56V.
Low power PoE Injector Applications (13W – 30W):
IP Cameras: A low power injector is commonly used to power Internet Protocol (IP) cameras and other surveillance systems like Network Video Recorders (NVRs).
Access Control Systems: PoE injectors can power access control devices such as card readers, keypads, door controllers, biometric fingerprint and facial recognition devices.
VoIP Phones: Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) phones and intercoms often utilize injectors to power individual phones in offices or call centers.
Point-of-Sale (POS) Systems: PoE injectors can power devices such as barcode scanners or card readers in retail environments.
Wireless Bridges: A low power injector would be great for powering a wireless bridge. It’s a networking device that connects two or more separate wired networks or network segments. Enabling communication between devices on each network as if they were directly connected by a physical cable, even if they’re located far apart and cannot be connected by traditional means.
Medium power PoE Injector & Midspan Applications (45W – 90W):
Small to Medium-Sized Networks: Medium power injector would have no problem powering a variety of devices in small to medium-sized networks and Network Attached Storage (NAS) hubs.
Digital Signs: PoE injectors are commonly used to power large digital displays, media players, and other small to medium-sized LED displays.
Building Automation Systems: PoE injectors can power sensors, actuators, and other building components, enabling centralized control and monitoring of various building functions such as lighting, HVAC, and security.
Monitoring Systems: A medium power option would be a great option for outdoor environmental monitoring systems, remote sensors, and IoT devices deployed outdoors or in harsh, secluded environments.
FAQ
Can Power over Ethernet power ventilators or defibrillators in the medical industry?
Currently, no. Due to these medical device’s substantial power requirements as well as compliance requirements, PoE is not implemented. However, as PoE technology advances, this may change in the future.
Can I use an indoor injector for an outdoor application?
Using an indoor PoE injector for outdoor applications is generally not recommended due to potential risks associated with environmental exposure. Outdoor environments pose challenges such as moisture, temperature variations, and UV exposure, which indoor PoE injectors are typically not designed to withstand. Outdoor-rated PoE injectors are specifically engineered with weatherproofing and electrical protections to ensure reliable operation and safety in outdoor settings. It’s crucial to use equipment that meets outdoor installation standards to mitigate risks of damage, electrical hazards, and performance issues in outdoor PoE installations.
Are there any security concerns associated with using PoE technology in smart cities?
Like any network, security measures are necessary for PoE systems. Secure protocols and proper switch configuration can mitigate security risks.
Related Articles
PoE Applications in Various Industries: Transforming Connectivity and Efficiency
Explore PoE applications revolutionizing connectivity in healthcare, education, and manufacturing, enhancing efficiency and cutting infrastructure costs.
Power over Ethernet Power: Exploring Wattage and Voltage Ranges for Optimized Performance in PoE Applications
Discover the ranges of power over Ethernet power, exploring how wattage and voltage variations meet diverse application needs effectively.
Power over Ethernet Explained: How PoE Revolutionizes Network Infrastructure for Modern Businesses
Explore how Power over Ethernet (PoE) transforms network infrastructure for modern businesses by simplifying installations, reducing costs, and enhancing flexibility for connected devices. Learn about its impact on efficient, scalable network solutions.


Selecting the Correct Equipment for your PoE Network
Selecting the correct equipment for your PoE network is essential for maximizing performance and efficiency. PoE technology combines data and power transmission over Ethernet cables, simplifying installations and lowering costs. Choosing the right PoE injectors, switches, splitters, and extenders depends on factors like network size, power demands, device compatibility, and environmental factors. This guide provides insights to help you make informed decisions, ensuring your PoE network meets current requirements and is scalable for future needs.
Legacy Install
When integrating PoE into an existing infrastructure (legacy install), compatibility is key. Ensure that your PoE equipment supports backward compatibility with older devices that may require lower power levels or different PoE standards. Upgrading to modern PoE injectors or switches that support both IEEE 802.3af/at/bt standards can facilitate seamless integration without the need for extensive retrofitting.
Greenfield Install
For new installations, integrating PoE lighting offers streamlined deployment and energy efficiency benefits. Using PoE switches that support IEEE 802.3bt (PoE++) standards enables powering high-efficiency LED fixtures over Ethernet cables. This approach simplifies installation complexity and supports advanced lighting controls such as occupancy sensing and remote management, aligning with sustainability goals while enhancing operational flexibility and cost savings.
When to use a Splitter
PoE splitters are useful when connecting non-PoE devices to a PoE network, separating power and data signals efficiently. Use splitters to retrofit legacy equipment with PoE capabilities, enabling cost-effective upgrades without replacing existing infrastructure.
When to use an Extender
PoE extenders enhance the reach of PoE networks beyond standard cable distances, ideal for large facilities or outdoor deployments where Ethernet cable lengths are over 100m. Choose extenders based on compatibility with PoE standards and desired transmission distances, ensuring seamless connectivity and power delivery to remote devices without compromising network performance.
Managed vs. Unmanaged Switch
The decision to use an unmanaged switch or a managed switch depends on your specific networking requirements, budget, and level of control needed over your network. Here’s a breakdown:
Unmanaged Switch:
Simplicity: Unmanaged switches are plug-and-play devices, requiring minimal setup. They are ideal for small networks or home environments where simplicity is key.
Cost-Effectiveness: Unmanaged switches are typically more affordable than managed switches, making them attractive for budget-conscious setups.
Limited Control: Unmanaged switches offer basic functionality without the ability to configure features such as VLANs, Quality of Service (QoS), or port mirroring.
Suitable for Small Networks: If you have a small network with a handful of devices and don’t require advanced network management features, an unmanaged switch is often sufficient.
Managed Switch:
Advanced Features: Managed switches provide a wide range of advanced features and configurations, including VLANs, QoS, link aggregation, port mirroring, and SNMP monitoring.
Granular Control: With a managed switch, you have granular control over your network, allowing you to optimize performance, security, and traffic prioritization.
Scalability: Managed switches are suitable for larger networks or environments where scalability and flexibility are important. They can accommodate growing network demands and complex setups.
Security: Managed switches offer enhanced security features such as Access Control Lists (ACLs) and port security, which help protect against unauthorized access and network attacks.
Network Monitoring: Managed switches often come with monitoring and troubleshooting tools, allowing you to diagnose network issues and optimize performance more effectively.
In summary, use an unmanaged switch for simple, cost-effective setups with minimal configuration needs. Opt for a managed switch if you require advanced features, granular control, scalability, security enhancements, or comprehensive network monitoring capabilities.
Passive vs. Active Injectors
The choice between using a passive injector and an active injector depends on your specific Power over Ethernet (PoE) requirements, device compatibility, and power management needs. Here’s a brief comparison to help determine when to use each type:
Passive Injector:
Benefits:
Cost-Effectiveness: Passive injectors are usually less expensive than active injectors, making them a budget-friendly choice for simple setups.
Simplicity: For small, straightforward installations where power requirements are known and do not need dynamic adjustment, a passive injector is sufficient.
Considerations:
Risk of Damage: Using a passive injector with devices not designed for it can damage the devices, as there is no handshake to ensure proper voltage and current.
Lack of Standards Compliance: Passive injectors do not adhere to IEEE PoE standards, so they should be used with caution and only with compatible equipment.
Active Injector:
Active injectors comply with IEEE PoE standards (such as 802.3af, 802.3at, and 802.3bt). They include a handshake process to negotiate power delivery with the PD, ensuring proper voltage and current are supplied.
Benefits:
Standards Compliance: When you need to ensure compatibility with IEEE PoE standards, providing a safer and more reliable power delivery method.
Device Protection: Active injectors protect devices by negotiating power requirements, preventing potential over-voltage or under-voltage issues.
Mixed Device Environments: Ideal for environments with a mix of PoE and non-PoE devices, as the injector will only supply power to PoE-compatible devices.
Advanced Features: Active injectors often support additional features such as power management, monitoring, and enhanced security.
Considerations:
Cost: Active injectors are typically more expensive than passive ones due to the additional technology and compliance with standards.
Complexity: They may require more setup and configuration compared to passive injectors.
In conclusion, use a passive injector for cost-effective, simple installations with devices specifically designed for passive PoE. Opt for an active injector when you need standards compliance, device protection, support for a variety of devices, and advanced power management features. Active injectors are generally the safer and more versatile choice for most PoE applications.
FAQ
Legacy vs. Greenfield Installation: What’s the difference between a legacy and greenfield PoE installation?
A legacy installation refers to adding PoE functionality to an existing network, while a greenfield installation involves designing a new network with PoE in mind from the start.
PoE Extenders: What does a PoE extender do and how does it differ from a PoE switch?
A PoE extender boosts the signal strength of a PoE connection, allowing you to reach devices farther away than standard Ethernet cables permit.
What does Greenfield mean, exactly?
A greenfield PoE installation refers to setting up a network entirely new. Imagine building on undeveloped land – there’s no existing infrastructure to deal with. This allows for maximum design flexibility when choosing PoE switches, injectors, and other equipment for your network. In software development, it means building a new system without needing to integrate with legacy systems. In business, it describes setting up new operations in a foreign country from the ground up. Greenfield projects offer the opportunity to design and implement without the limitations of existing structures or systems.
What specific features do I need in my network (VLANs, QoS, etc.) to justify the cost of a managed switch?
A managed switch is worth the investment if you need features like VLANs (separating network traffic), Quality of Service (QoS) for prioritizing critical applications, or advanced security controls. If your network is simple and performance isn’t a major concern, an unmanaged switch might suffice.
If I plan to expand my network in the future, will an unmanaged switch limit me or can I upgrade to a managed switch later?
Unmanaged switches can limit future scalability. While upgrading to a managed switch later is possible, it requires purchasing new equipment and reconfiguring your network. Consider a managed switch from the start if future expansion is likely.
Related Articles
How to Build a Future-Proof Ethernet Infrastructure: Designing and Implementing a Reliable PoE Network for Modern Businesses
Learn how to design a new PoE ethernet infrastructure from the ground up, with a focus on selecting the latest standards and equipment.
PoE Splitter: The Complete Overview of PoE Splitters in Network Installations
Discover the scenarios where a PoE splitter is necessary, and how it can enable you to power non-PoE devices effectively while maintaining data integrity.
PoE Extender: Exploring Applications for Network Expansion
Explore the advantages of PoE extenders in extending network reach beyond 100 meters, ensuring reliable power and data connections.
PoE Switch: Choosing Between Managed vs. Unmanaged for Your Network Needs
Compare managed and unmanaged PoE switches to determine the best fit for your network’s size and control needs. Gain insights to make informed decisions.
Active vs Passive PoE Injectors: Understanding the Key Differences
Learn about the differences between passive vs active PoE injectors, including their operating principles and how to choose the right type for safe and efficient power delivery to your devices.
Choosing the Right PoE Injector: A Comprehensive Guide
This guide provides an in-depth look at selecting the ideal PoE injector for your network needs, covering key factors such as power requirements, compatibility, and performance features.
Phihong’s PoE Products, Manufacturing Capabilities, and Key Benefits
Phihong carries over 50 different types of Power Over Ethernet products and peripherals, including; PoE Injectors, PoE Splitters, Media Converters and Poe-to-USB-C products that are fully IEEE802.3af (PoE), IEEE802.3at (PoE+), and IEEE802.3bt (PoE++) compliant:
Phihong’s PoE Product Solutions
PoE Injectors
Phihong offers indoor and outdoor IEEE802.3af, IEEE802.3at, and IEEE802.3bt standards-based, as well as passive, injectors from 15.4W – 90W of power with data speeds from 1G – 10G. Outdoor, high surge capable, 24VAC input and DC input models are also offered.
Media Converters
IEEE802.3bt compliant 60W 1G compatible fiber to copper media converter.
Splitters
IEEE802.3af, IEEE802.3at and IEEE802.3bt compliant splitters.
PoE-to-USB C
20W IEEE802.3at and 60W IEEE802.3bt compliant PoE-to-USB C converters.
Click to View Our Power Over Ethernet Product Page
Phihong’s Custom PoE Solutions for OEMs
Phihong excels in delivering custom Power over Ethernet (PoE) solutions tailored for OEMs and large-scale projects, showcasing their expertise in meeting specific requirements and addressing unique challenges. With a proven track record, Phihong has successfully engineered PoE solutions for various applications, ensuring optimal performance, efficiency, and reliability. For instance, in past projects, Phihong has designed specialized PoE systems that integrate seamlessly into complex infrastructures, enhancing operational efficiency and enabling advanced functionalities. Their commitment to innovation and quality ensures that each custom solution not only meets but exceeds client expectations, setting a benchmark in the industry for robust and adaptable PoE solutions.
Phihong’s General Competitive Advantages
+50 Years in the Industry
For over five decades, Phihong has been a beacon of reliability in the power electronics industry, with a rich legacy dedicated to excellence. At the heart of Phihong lie its core values—efficiency and reliability—ingrained in every custom product Phihong delivers..
Key Role in IEEE Standardization
As the sole power supply manufacturer member on the IEEE PoE committees, Phihong has played a pivotal role in advancing PoE standards. From contributing to the development of AT/BT standards to actively participating in future IEEE PoE standards discussions, Phihong remains at the forefront of innovation in the Power Over Ethernet ecosystem.
Phihong’s PoE Patent
Phihong’s Patent No US 11.005.670 B2 represents a significant advancement in Power over Ethernet technology, showcasing innovative solutions that enhance the efficiency and reliability of PoE systems. Owning this patent highlights Phihong’s leadership and expertise in the field, ensuring that OEMs benefit from cutting-edge technology and robust intellectual property protection. Partnering with Phihong allows OEMs to leverage this proprietary technology, ensuring their products stand out in a competitive market with superior performance, compliance with regulatory standards, and enhanced customer satisfaction.


High Product Efficiency
Efficiency is a distinguishing feature of Phihong’s PoE injectors, with unparalleled efficiency meeting DOE VI standards (required to sell in the U.S.). Our dedication to innovation is also evidenced by models that meet future DOE VII requirements.
Reliability
Reliability is paramount in Phihong’s PoE products, which boasts conservative component ratings. Our commitment to reliability is further evidenced by designs ensuring a minimum 3-year Electrolytic Capacitor (Ecap) life at maximum temperature and load, minimizing field failures and returns.
ONE YOU CAN TRUST!






























“Great project management. It feels good to know that many eyes and hands are taking care of our requirements until full completion.”

Phihong’s Competitive Advantage: Vietnamese Manufacturing Facilities
Reduced Risk
Phihong has manufacturing facilities in Vietnam. By diversifying power supply manufacturing away from China, OEM clients can effectively mitigate a range of risks, including concerns related to political instability and trade conflicts that may lead to disruptions in production or shipping lead times.
By reducing dependency solely on China, OEMs can enhance their protection in the face of such challenges, ensuring continuity in supply chains and minimizing the impact of unforeseen disruptions.
Unfortunately, over recent years, the relationship between China and the U.S. has become strained, marked by the imposition of tariffs and allegations of unfair trade practices. Therefore, working with power supply manufacturers like Phihong, who are proactive in facing such challenges by taking steps towards owning manufacturing facilities outside of China spells a competitive advantage for OEMs.
Cost Savings
In Vietnam, competitive labor costs stand out as a significant advantage compared to numerous other global manufacturing destinations. This cost efficiency stems from various factors such as Vietnam’s lower wage rates, favorable labor regulations, and a growing workforce.
Additionally, products made in China are subject to a 25% tariff, whereas there are no tariffs for products made in Vietnam. Opting for products made in Vietnam helps avoid these costly tariffs.
Favorable Marketing Advantage
Some OEMs may prefer working with power supply manufacturers that manufacture outside of China due to labor practices, intellectual property protection or environmental concerns. It might be something an OEM client would want to market to their customers as a positive feature.
Comprehensive Trade Agreement
The U.S. and Vietnam have what is called a Bilateral Trade Agreement (BTA), which was signed in 2000 and entered into force in 2001 (USTR Vietnam Trade Agreement). This agreement covers a wide range of areas including:
- Reduced tariffs on goods traded between the two countries
- Protections for intellectual property rights
- Increased market access for service providers
Unfortunately, the U.S. and China do not currently have a comprehensive bilateral trade agreement like the U.S. has with Vietnam. However, they do have a multilateral trade agreements:
Phase One Deal (2020): This agreement aimed to address some trade issues, like intellectual property theft. It included China agreeing to purchase more U.S. goods and the U.S. reducing some tariffs. (https://ustr.gov/phase-one).
World Trade Organization (WTO) agreements: Both China and the U.S. are members of the WTO, which sets basic rules for international trade. This provides a framework for their trade relationship. (https://www.wto.org/english/thewto_e/whatis_e/tif_e/agrm1_e.htm).
The BTA offers a deeper and more tailored trade relationship between the U.S. and Vietnam compared to the general framework provided by the WTO for the U.S. and China (including the Phase One Deal).
Phihong’s U.S. Centered Facility: Key Benefits
Phihong is a global company with headquarters in Taiwan, but Phihong’s manufacturing, R&D, and sales facilities are spread out worldwide. Though not solely U.S.-based, Phihong’s U.S. presence offers advantages for many OEMs seeking to serve the American market:
U.S. Inventory
Better lead times are further bolstered by their Fremont, California inventory hub, situated in the heart of Silicon Valley. Having an inventory facility close to OEMs in a region teeming with technology giants offers a significant advantage to Phihong’s partners in the telecom, datacom, and personal electronics industry. The Fremont facility goes beyond inventory storage, serving multiple purposes to enhance convenience for U.S. OEMs.
U.S. R&D
Phihong’s U.S. hubs located in California and New York serve as research and development (R&D) centers, providing significant advantages to U.S. OEMs. Close proximity is the key benefit for U.S. based OEMs, translating into more efficient interactions, reducing the need for overseas travel and minimizing the time and cost associated with managing different time zones. Moreover, Phihong’s R&D teams in these locations possess a deep understanding of local market dynamics and U.S. regulatory requirements.
U.S. Customer Support
Having local customer and product engineer support is just another benefit when it comes to working with a power supply manufacturer like Phihong. This translates into faster response times for inquiries, no language barriers to worry about or significant time zone differences to navigate. When business partners call our dedicated line at (510) 445-0100 during business hours, they will have the opportunity to speak directly with one of our knowledgeable application engineers or associates.
Our support team is available Monday through Friday, from 9:30am to 6:30pm PST, whether you have inquiries about our products, need technical guidance, or require assistance with troubleshooting.
11 Key Advantages Working With Phihong
+50 Years in the Industry
Phihong Played a Key Role in IEEE
High Product Efficiency
Reliable
Reduced Risk in Vietnam
Cost Savings in Vietnam
Favorable Marketing Advantage for OEMs
Comprehensive Trade Agreement
U.S. Inventory Facilities
U.S. R&D
U.S. Customer Support
FAQ
Can Phihong provide custom PoE solutions?
Yes, Phihong specializes in custom PoE solutions tailored for OEMs and large-scale projects, designed to meet specific requirements and address unique challenges. We hold patents on PoE technology and are capable of developing new solutions from scratch. Phihong collaborates closely with OEM partners from beginning to end, tailoring PoE products to contain specific features, to optimize performance, and to ensure seamless compatibility.
Where are Phihong’s manufacturing facilities located?
Hai Phong, Vietnam and Dongguan, China.
Where are Phihong’s research and development buildings located?
Taoyuan, Taiwan; Tainan, Taiwan; Fremont, California; Bohemia, New York.
Related Articles
Ethernet PoE Injector: Why Phihong Leads in PoE Technology: A Deep Dive into Their Products and Manufacturing
Discover Phihong’s Ethernet PoE Injector lineup tailored to fulfill diverse power over ethernet requirements in this informative article.
PoE Architecture: Phihong’s Custom PoE Solutions – A Perfect Fit for Your Designs
Explore Phihong’s tailored PoE architecture solutions, crafted to meet the distinct needs of Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs).
PoE Manufacturer Phihong’s U.S. and Vietnamese Facilities Become an OEM Advantage
Discover how PoE manufacturer Phihong’s facilities in Vietnam and the U.S. are driving efficiency and competitive pricing in the western PoE market.
PoE Production: Exploring Phihong’s Competitive Edge and Overall Strengths
Discover how Phihong’s PoE production expertise sets them apart with innovative strengths and a competitive edge in the industry.
Why Phihong’s Shift from China to Vietnam and the U.S. is a Game Changer for PoE Manufacturing
Learn why Phihong’s move from China to Vietnam and the U.S. is transforming PoE manufacturing with enhanced quality and efficiency.


Designing Your PoE Network System Correctly
Designing your PoE network system correctly involves careful consideration of several key factors to ensure optimal performance and reliability
Ventilation
Adequate ventilation is crucial for PoE equipment to dissipate heat effectively, especially in enclosed spaces or racks with multiple devices. Proper airflow helps prevent overheating, which can degrade equipment performance and reliability over time. It’s essential to design network cabinets or installation spaces with sufficient airflow, considering factors like device placement and ambient temperature.
Distance Between PSE & PD
The distance between the Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE) and Powered Devices (PD) affects power delivery efficiency and data transmission reliability. Longer distances can result in voltage drop and signal degradation, impacting network performance. To mitigate these issues, choose PoE equipment and Ethernet cables that support the required distance without compromising power delivery or data integrity. Factors such as cable type (Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a), cable quality, and PoE standard (e.g., IEEE 802.3af/at/bt) influence maximum allowable distances.
Power Drop Between PSE & PD
Power drop occurs as electrical current travels through Ethernet cables, especially over longer distances or cables with higher resistance. Managing power drop is critical to ensuring that the PD receives sufficient power for optimal operation. Calculating power drop based on cable length, gauge, and current load helps determine appropriate cable specifications and ensures required power is available to the PD.
Efficiency
PoE system efficiency refers to how effectively power is delivered and utilized across the network. Efficient designs minimize energy loss and maximize power utilization, contributing to lower operating costs and reduced environmental impact. Factors influencing efficiency include the choice of PoE equipment (e.g., high-efficiency PSEs and PDs), power management strategies, and adherence to energy-saving practices such as using energy-efficient Ethernet (EEE) and powering down unused ports. Additionally, using the highest gauge cable to minimize losses is crucial, as high-quality cables ensure optimal power transmission with minimal voltage drop and heat generation, further enhancing the overall efficiency and reliability of the PoE system.
Regulatory Considerations
Compliance with regulatory standards (e.g., UL, CE, FCC) ensures PoE equipment meets safety, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), efficiency regulations (DOE), and interoperability requirements in different regions. Adhering to these standards not only ensures legal compliance but also minimizes risks associated with electrical hazards, interference, and compatibility issues in PoE installations.
Environmental Factors (Temperature, Surge)
PoE equipment should be designed to operate reliably in various environmental conditions, including temperature extremes and potential electrical surges. Components rated for wide temperature ranges (-40°C to 75°C or higher) ensure stability in both indoor and outdoor deployments. Surge protection mechanisms safeguard against transient voltage spikes, protecting PoE devices from damage and ensuring continuous operation in unpredictable electrical environments.
Active vs Passive PoE Injectors
Active PoE components incorporate electronics to manage power delivery and communication between PSE and PD, offering safety, flexibility and control over power levels. In contrast, passive PoE components deliver power without negotiation or management, suitable for simpler applications with fixed power requirements. Choosing between active and passive components depends on application needs, power budget considerations, and compatibility with existing infrastructure.
Managed vs Unmanaged Switches
Managed PoE switches offer advanced features such as VLANs, Quality of Service (QoS), and remote management capabilities, providing flexibility and control over network traffic and device prioritization. Unmanaged switches are plug-and-play solutions that offer simplicity and cost-effectiveness for smaller networks or applications where basic connectivity is sufficient. Choosing between managed and unmanaged switches depends on network complexity, scalability needs, and IT management capabilities.
Single vs Multiport Devices
Single-port PoE devices are suitable for powering individual PDs or devices requiring dedicated power connections. Multiport PoE devices (e.g., switches, midspans) support multiple PoE-enabled ports, enabling centralized power distribution and connectivity for multiple devices from a single unit. Selecting the appropriate device type depends on the number of PDs to be powered, network expansion plans, and infrastructure layout requirements.
Network Cables
Data Rate vs Cable Length vs Cable Type
PoE equipment should support data rates compatible with network requirements, including Gigabit Ethernet (10/100/1000/2500 Mbps) and higher speeds (5-10 Gbps). Matching PoE switches, injectors, and cables to the required data rate ensures optimal network performance, supporting bandwidth-intensive applications and future scalability.
Shielded or Unshielded Cables
Shielded cables are recommended for Power over Ethernet (PoE) applications in environments with high levels of electromagnetic interference (EMI) or radio frequency interference (RFI). Here are some scenarios where using shielded cables for PoE is beneficial:
Industrial Environments: In industrial settings where machinery, equipment, and electrical devices generate significant EMI or RFI, shielded cables can help mitigate interference and ensure reliable power and data transmission for PoE-enabled devices.
Outdoor Installations: Outdoor installations are exposed to environmental factors such as moisture, temperature fluctuations, lightning strike/surge voltage, and electromagnetic radiation from nearby power lines or radio equipment. Shielded cables provide additional protection against EMI and RFI, ensuring stable performance for outdoor PoE devices like surveillance cameras and wireless access points.
High-Density Deployments: In environments with high-density deployments of PoE devices, such as data centers or office buildings, shielded cables can help reduce crosstalk and interference between adjacent cables, minimizing signal degradation and ensuring consistent power delivery and data transmission.
Long Cable Runs: For long cable runs, especially those running parallel to power cables or other sources of interference, shielded cables can prevent signal degradation and maintain PoE performance over extended distances.
Critical Infrastructure: In mission-critical applications where uninterrupted power and data connectivity are essential, such as healthcare facilities, transportation systems, or security operations centers, shielded cables provide an extra layer of protection against EMI and RFI-induced disruptions.
Overall, while shielded cables may be more expensive than unshielded alternatives, they offer superior protection against interference and can help ensure the reliability and performance of PoE installations in challenging environments. When planning a PoE deployment, assess the environmental conditions and potential sources of interference to determine whether shielded cables are necessary to maintain optimal performance and reliability.
Types of Network Cables
For Power over Ethernet (PoE) applications, you can use various types of network cables, but the most common and recommended ones are:
Category 5e (Cat5e): Cat5e cables are suitable for most PoE applications, providing sufficient bandwidth and power delivery capability for standard PoE (IEEE 802.3af), PoE+ (IEEE 802.3at), and POE++ (IEEE 802.3bt) deployments. They support data rates up to 1 Gbps and are widely available and cost-effective.
Category 6 (Cat6): Cat6 cables offer higher performance compared to Cat5e, with improved shielding and reduced crosstalk. They are suitable for all PoE standard applications and can handle higher data rates up to 5 Gbps over shorter distances. Cat6 cables provide better performance and reliability, making them a preferred choice for demanding PoE installations.
Category 6a (Cat6a): Cat6a cables are an enhanced version of Cat6, offering even higher performance and bandwidth. They support data rates up to 10 Gbps over longer distances and provide superior noise immunity and signal integrity. Cat6a cables are ideal for high-speed PoE applications and future-proofing your network infrastructure.
Category 7 (Cat7): Cat7 cables are designed to support even higher data rates and frequencies than Cat6 and Cat6a. They offer improved shielding and reduced interference, making them suitable for demanding PoE applications in environments with high electrical noise or electromagnetic interference.
When selecting a network cable for PoE applications, ensure that it meets the necessary standards for power delivery and data transmission, and consider factors such as cable length, environmental conditions, and installation requirements. Additionally, it’s essential to use high-quality, certified cables from reputable manufacturers to ensure reliable performance and safety for your PoE-enabled devices.
PoE Installation
PoE installation refers to the process of setting up a network that utilizes PoE technology. This involves installing PoE switches or injectors, running Ethernet cables to PoE-enabled devices, and configuring the network for optimal performance. PoE installation simplifies the deployment of network devices by reducing the need for separate power sources, streamlining the setup process, and enhancing overall network efficiency.
PoE Troubleshooting
PoE troubleshooting involves diagnosing and resolving issues like insufficient power delivery, device compatibility, and cable faults. Effective troubleshooting requires understanding PoE standards, using diagnostic tools, and following best practices. Key compatibility issues include whether the powered device is passive or standards-based, its power requirements, the use of shielded cables, and cable length. Addressing these ensures reliable operation and optimal performance of PoE-enabled devices and networks.
Common Troubleshooting Scenarios
Are you trying to use a passive or active injector? Is the powered device IEEE802.3 standards based?
What is the stated output voltage of the injector? Passive injectors are not necessarily with 48V or 56V output.
Is the length of the run from the switch to the powered device within 100 meters? Maximum length is 100 meters or data integrity is compromised.
There is cable voltage drop along the run of the cable due to resistance (IR drop). With IEEE802.3af the output voltage from the injector should be from 44V to 57V with output power of 15.4W. However, with the IR drop across the cable the minimum power at the powered device should be no less than 12.95W. With IEEE802.3at power at the power sourcing equipment is 30W but at the powered devices is 25.5W. With IEEE802.3bt at 60W at the power sourcing equipment power at the powered device should be 51W and for 90W at the power sourcing equipment power should be no less than 71.3W at the powered device. (Need to account for voltage drop with passive injectors as well._
What type of Ethernet cable is used? IEEE802.3at and IEEE802.3bt require Cat5e or Cat6 cables. IEEE802.3af/at/bt can use Cat 5.
FAQ
How does inadequate ventilation impact the performance and lifespan of PoE devices?
Inadequate ventilation can cause overheating in PoE devices, leading to reduced efficiency, increased failure rates, and shortened lifespan due to thermal stress on components.
How much airflow does my PoE switch require for proper cooling?
The required airflow depends on the switch’s model and wattage. Consult the manufacturer’s specifications for recommended airflow and avoid placing the switch in enclosed spaces without proper ventilation.
Are there any safety regulations I need to follow when installing a PoE network system?
Yes, adhere to local electrical safety codes. PoE equipment should be certified to meet safety standards like UL or IEC.
Should I choose a single-port PoE injector or a multiport PoE switch?
A single-port injector is suitable for one device. For multiple PoE devices, a multiport PoE switch offers a more centralized and scalable solution.
What type of network cable should I use for a PoE network?
For a standard PoE network, Cat5e or Cat6 would suffice. However with 10G networks, Cat7 is recommended.
Related Articles
PoE Ethernet Extender: Understanding Distance Limitations Between PSE and PD
Explore how voltage drop affects power delivery, network reliability, and performance in PoE systems with a PoE Ethernet Extender.
PoE Power Over Ethernet Efficiency: Strategies for Power Saving and Cost Reduction
Learn cost-effective methods to enhance power efficiency in PoE Power Over Ethernet networks.
PoE Compliance: Navigating Safety and Regulatory Considerations for Efficient Network Deployment
This article covers key PoE compliance regulatory standards that ensure PoE equipment meets safety, efficiency, and interoperability requirements.
Multiport PoE Injector vs. Single PoE Injector: Choosing the Right Device for Your Network
Compare Multiport PoE Injector vs. Single PoE Injector to find the optimal device for network efficiency and scalability in your infrastructure.
PoE Cables: Choosing the Best Network Cables
Learn about different types of PoE cables: Cat6, Cat7, shielded vs. unshielded, their data rates, and how to choose the best option for your PoE network.
Power over Ethernet Design: Mastering Effective Network Planning and Implementation Strategies
Explore Power over Ethernet Design for expert strategies in planning and implementing efficient network infrastructures.
PoE Troubleshooting: Addressing Common Issues in PoE Network Deployment
Discover effective strategies for PoE troubleshooting to resolve common issues in network deployment, ensuring smooth operation and reliability.


Contact Our Team Today!
Our dedicated sales team and international partners are prepared to support you with your latest projects and initiatives globally.
Energy Efficiency Standards and Your PoE Network
What Are Energy Efficiency Standards?
Energy efficiency standards for Power over Ethernet (PoE) and PoE injectors encompass several international regulations. In the US, the Department of Energy (DOE) sets efficiency benchmarks for electronic devices, including PoE equipment. Canada’s Natural Resources Canada (NRCan) enforces similar standards to ensure energy-efficient operations. Europe’s Ecodesign EU 2019/1782 regulates passive PoE injectors. Australia’s Greenhouse and Energy Minimum Standards (GEMS) and New Zealand’s Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) mandate specific efficiency levels to reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Compliance with these standards ensures that PoE systems operate with minimal energy wastage, supporting both economic and environmental goals.




What Equipment Within the PoE Network Needs to Meet Energy Efficiency Standards?
In the U.S., within a PoE network PoE injectors need to comply with efficiency standards. Additionally, network infrastructure components, including cables and connectors, should be designed to minimize power loss and ensure efficient power transmission. Ensuring that all these components meet energy efficiency standards helps optimize the overall performance and energy consumption of the PoE network.
How to Measure Efficiency
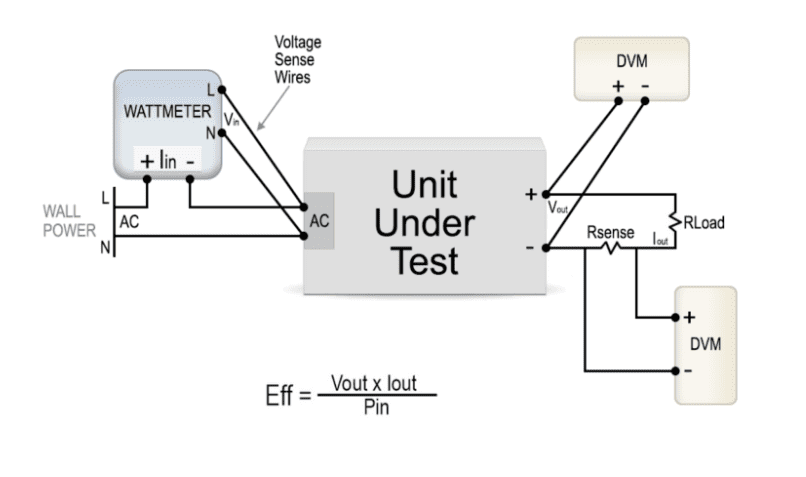

Types of Energy Efficiency Standards
U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)
External power supplies manufactured and distributed in commerce, as defined by 42 U.S.C. 6291(16), must meet the energy conservation standards specified in the Code of Federal Regulations at 10 CFR 430.32(w). The Department of Energy (DOE) sets energy efficiency-standards and test procedures for residential, commercial, and industrial products. DOE is required to review these standards and test procedures periodically, and initiates a process to set new standards provided that improvements to energy efficiency are “technically feasible and economically justified.”
DOE Level VI: This is a standard set by the U.S. Department of Energy, which went into effect February 10, 2016, to regulate energy efficiency in external power supplies. It requires these power supplies to meet stringent efficiency standards, particularly in reducing standby power consumption when devices are not in use. Compliance with Level VI ensures that power supplies are energy-efficient, helping to lower electricity usage and reduce environmental impact.
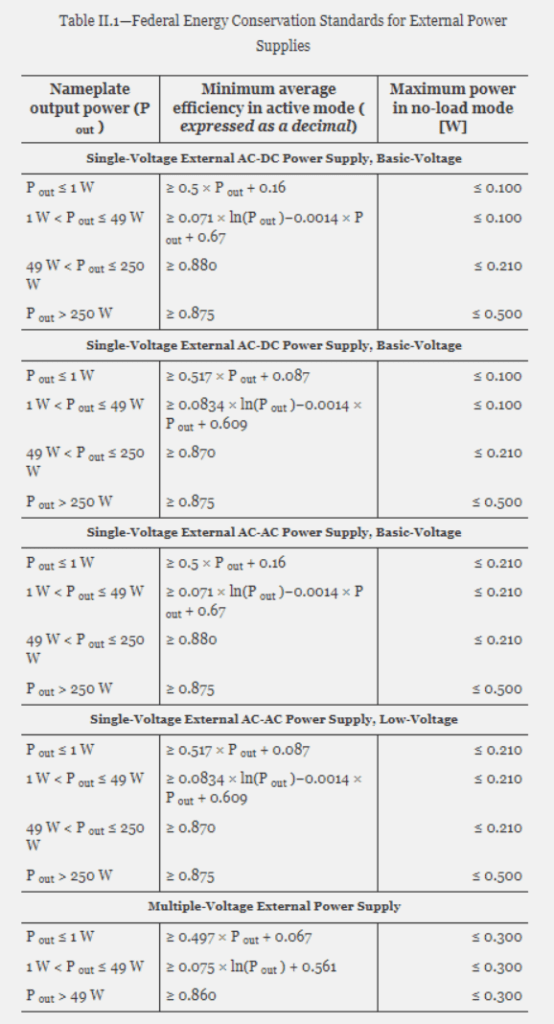

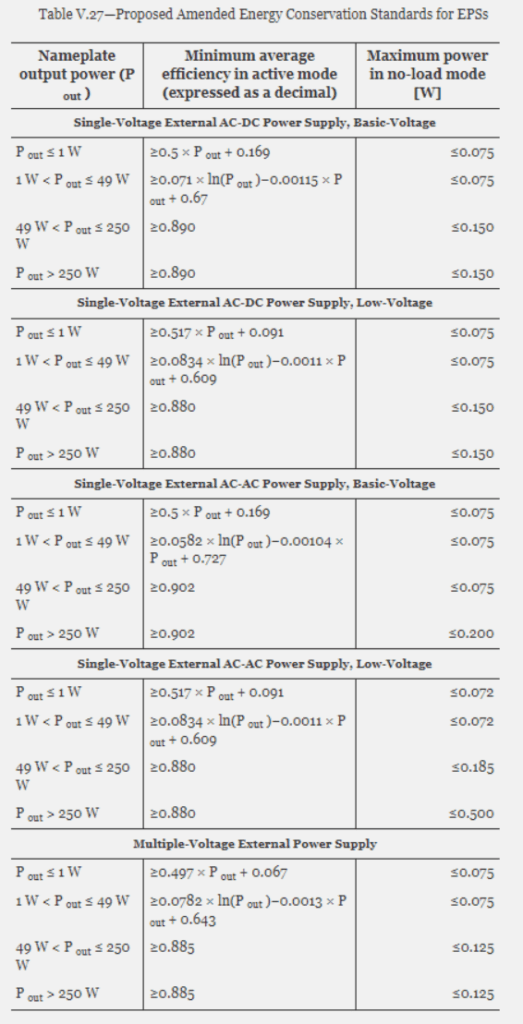
DOE Level VII: In February 2023 the US Department of Energy issued a notice of proposed rulemaking regarding energy conservation standards for external power supplies. The new proposed standard, DoE Level VII, if deemed both technologically feasible and economically justified, would impose more stringent energy conservation standards upon external power supplies. This would require manufacturers to meet higher average efficiency levels and lower no-load energy consumption levels, as outlined in the below table, two years after publication as a final rule in the Federal Register.

Natural Resources Canada (NRCan)
All regulated products, including PoE injectors, under Canada’s Energy Efficiency Act and Energy Efficiency Regulations must meet federal energy efficiency standards to be imported into Canada or shipped from one province to another for the purpose of sale or lease. As of July 1, 2017 PoE injectors must meet the same minimum energy performance standards as those for Level VI compliance in the U.S.
EU Ecodesign 2019/1782
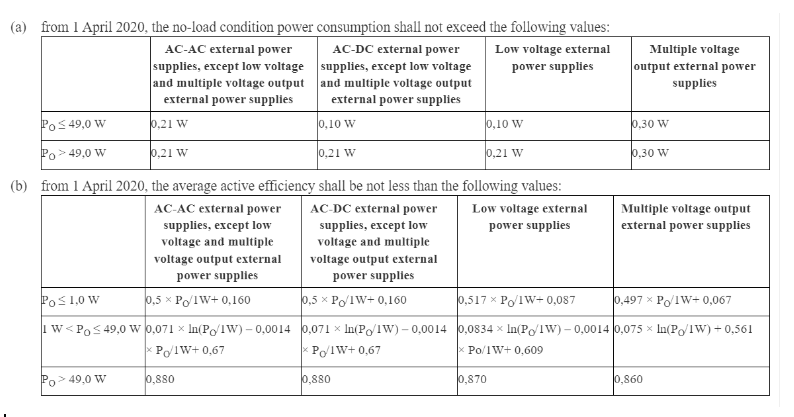
Published 1 October 2019, EU 2019/1782 updated the regulations covering external power supplies with an output power up to 250W that are intended to work with electrical and electronic household and office equipment. The rules apply to both active efficiency when a power supply is connected to a device and no-load power consumption when the power supply is plugged into a power outlet but not connected to a device. Currently only passive PoE injectors need to comply with European Ecodesign requirements.

Australia Greenhouse and Energy Minimum Standards Act 2012 (GEMS) and New Zealand Energy Efficiency (Energy Using Products) Regulations 2002
Though not as stringent as the U.S.’s DoE Level VI or Europe’s Ecodesign, Australia and New Zealand require that appliances and equipment, such as PoE injectors, meet or exceed minimum levels of energy performance before they can be supplied or used for commercial purposes.
FAQ
What is the significance of compliance with DOE Level VI and the proposed DOE Level VII standards for PoE injectors?
DOE Level VI compliance is required of external power supplies, including injectors, by the U.S. Department of Energy (DoE). Compliance ensures high energy efficiency and low standby power, reducing electricity usage and environmental impact. DOE Level VII, if adopted by the DoE, will set even higher efficiency standards, further enhancing energy savings and sustainability.
Related Articles
PoE Standards: Understanding Energy Efficiency Standards for PoE Injectors
Demystifying energy efficiency PoE standards and what they mean for Power Over Ethernet products.
DoE Level VII: The New Energy Dept Standard and its Effect
This article explores the Department of Energy’s Level VII standard, detailing its new energy efficiency requirements and their impact on power supplies and overall energy consumption.
Safety, Quality, Facility Standards and Ratings
Types of Regulatory Compliance Standards


Safety Compliance
For the US market, UL (Underwriters Laboratories) provides various ratings for electrical devices, including PoE injectors. These ratings may include UL-Listed, UL Recognized, or UL Certified, indicating compliance with specific safety and performance standards. PoE midspans should be evaluated to and comply with standard UL 62368-1 for the United States. Look for the UL-Listed mark.


For Canada PoE injectors will need to be evaluated to and certified to CSA 22.2 No. 62368-1 for Canada.
For Europe, the low voltage directive (LVD) (2014/35/EU) ensures that electrical equipment within certain voltage limits provides a high level of health and safety risk protections for European citizens. PoE injectors should be evaluated to comply with standard IEC 62368-1 by a certification organization. Compliance to the standard is one of the requirements to apply the CE mark on a PoE injector for sale in Europe.
The IECEE Certification Body scheme is an international system for mutual acceptance of test reports and certificates dealing with the safety of electrical and electronic components, equipment, and products, such as PoE injectors, by participating member countries and certification organizations. The scheme is operated by the IEC System of Conformity Assessment Schemes for Electrotechnical Equipment and Components (IECEE). Typically, most manufacturers will apply for the certification body scheme with the IEC 62368-1 low-voltage certification.
EMISSIONS
For the U.S., FCC compliance is crucial for Power over Ethernet (PoE) injectors and products, ensuring they meet regulatory standards set by the Federal Communications Commission. PoE injectors, which enable the transmission of power and data over Ethernet cables, must adhere to FCC Part 15 guidelines to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensure they operate within allowable frequency limits.
Compliance involves rigorous testing to certify that devices do not interfere with other electronic equipment and operate safely within specified power levels. This adherence not only ensures product reliability but also legal market access, reassuring consumers of quality and safety standards in PoE technology. Look for the FCC statement on the device stating “This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation,” as well as where one may access the Supplier’s Declaration of Conformity.
For Canada PoE injectors will need to comply with ICES-003 and compliant devices will bear an ISED compliance label, such as CAN ICES-003(B) / NMB-003(B), as an example.
For Europe EN 55032 is the standard that specifies the electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) requirements for multimedia equipment. It sets limits and methods of measurement for the emission of radio frequency disturbances to ensure that electronic devices do not interfere with other equipment or radio services. EN 55032 covers a wide range of multimedia devices including audio, video, broadcast receivers, and similar apparatus. Compliance with EN 55032 certification standards ensures that products meet stringent criteria for electromagnetic compatibility, thereby minimizing electromagnetic interference and ensuring reliable operation in various environments. Compliance to EN 55032 is needed to meet EU EMC Directive 2014/30/EU and is another requirement to mark CE on a PoE injector for sale in Europe.
Immunities
EN 55035 is an Immunity Standard in Europe for Information Technology Equipment, consumer electronics such as audio video equipment, and broadcast equipment within a multimedia technology equipment standard and defines tests that are designed to enable manufacturers to demonstrate that their equipment is designed to withstand interference placed upon it either through the air or through any connected cables. This standard is applicable to multimedia equipment with an AC or DC supply voltage rating of 600V or less. Compliance to EN 55035 is also needed to demonstrate compliance to EU EMC Directive 2014/30/EU and is another one of the requirements to mark CE on a PoE injector for sale in Europe.
RoHS
RoHS stands for Restriction of Hazardous Substances. It is a directive adopted by the European Union (EU) that restricts the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment (EEE). The directive aims to reduce the environmental impact of EEE by prohibiting or limiting the use of substances such as lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, polybrominated biphenyls (PBB), and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDE).
RoHS compliance ensures that products sold in the EU market are free from these hazardous substances, thereby promoting environmental sustainability and protecting human health. Manufacturers must adhere to RoHS standards and conduct testing and documentation to demonstrate compliance before placing their products on the market. RoHS has become a global standard, influencing regulations and practices beyond the EU, impacting how electronic products are designed, manufactured, and disposed of worldwide. Compliance with RoHS requirements is a requirement to Declare Conformity with European requirements and to place a product, such as a PoE injector, for sale in the European market.
ISO Facility Standards
ISO 14001 (Environmental)
ISO 14001 is an international standard that specifies requirements for an environmental management system (EMS). It provides a framework for organizations to systematically manage their environmental responsibilities, enhance environmental performance, and achieve environmental sustainability goals. In the context of Power over Ethernet (PoE) injectors, compliance with ISO 14001 means that manufacturers and users of these devices should implement practices to minimize environmental impacts throughout the lifecycle of the injectors. This includes design considerations to reduce energy consumption, materials selection to minimize waste generation, and adherence to regulations related to hazardous substances. By integrating ISO 14001 principles into their operations, companies can demonstrate their commitment to environmental stewardship and sustainability.
ISO 9001 and 9002 (Quality)
ISO 9001 and ISO 9002 are standards that outline requirements for quality management systems (QMS). ISO 9001 focuses on general QMS requirements, emphasizing consistent product and service quality and customer satisfaction. ISO 9002, which was merged into ISO 9001 in 2000, specifically addressed production and installation aspects within the QMS framework.
When applied to Power over Ethernet (PoE) injectors, compliance with ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers and users maintain rigorous quality control processes throughout the lifecycle of these devices. This includes adhering to standards for design, production, testing, installation, and service of PoE injectors, ensuring reliability, safety, and performance consistency. ISO 9001 also promotes continuous improvement and customer focus, ensuring that PoE injectors meet or exceed customer expectations.
Overview of PoE Ratings
IP, NEMA and IK Ratings
Ingress Protection (IP) ratings on PoE injectors classify their ability to resist intrusion from contaminants like water and dust, crucial for outdoor use. These ratings, ranging from IP00 (no protection) to IP69K (complete protection against internal contamination), indicate varying degrees of safeguarding. For instance, IP67, the most common rating, breaks down as follows: the “6” signifies complete dust-tight protection, ensuring no ingress of dust particles into the injector’s external case. Meanwhile, the “7” denotes water resistance, specifying protection against immersion up to 1 meter depth for 30 minutes without adverse effects. Higher numbers like “8” and “9” would imply protection against prolonged immersion and complete water ingress resistance, respectively. PoE injectors with robust IP ratings are indispensable for outdoor deployment, where exposure to harsh conditions demands reliable performance and longevity, safeguarding both power and data transmission capabilities against environmental elements.
The National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) provides ratings for defining the types of environments in which electrical enclosures can be used and their ability to withstand certain environmental conditions, such as dust, water, corrosion, and impacts.
IK Ratings
The IK rating measures the degree of protection provided by electrical enclosures against mechanical impacts, such as vandalism or accidental damage. IK ratings range from IK01 to IK10.
FAQ
How do IP, UL, NEMA, and IK ratings specifically impact the selection and deployment of PoE injectors in different environments?
IP ratings indicate dust and water protection, UL ratings certify safety standards, NEMA ratings show protection against environmental factors, and IK ratings measure resistance to physical impacts, all critical for selecting PoE injectors for specific environments.
What are the practical implications of choosing standards-based PoE injectors over passive injectors for network safety and reliability?
Standards-based PoE injectors ensure safe, reliable power delivery with built-in protections, preventing overloading and compatibility issues, whereas passive injectors lack these safeguards, posing safety and reliability risks.
How can you tell if a PoE system is high quality?
While there’s no single quality standard, reliable PoE systems typically follow IEEE 802.3 standards, deliver enough power for your devices, come from a reputable brand, and have safety, emissions and efficiency certifications.
Are there relevant ISO facility standards for PoE deployments?
Yes, although ISO standards don’t directly govern PoE, some can be helpful. For instance, ISO/IEC 29110 provides cabling guidelines, ISO 11404 helps with air quality for PoE devices sensitive to temperature, and ISO 27001 offers a framework for information security in PoE deployments with sensitive data.
What do the different PoE ratings (e.g., PoE, PoE+, PoE++ ) mean?
PoE ratings indicate the maximum power a PoE switch can deliver. PoE (IEEE 802.3af) provides up to 15.4W, PoE+ (IEEE 802.3at) goes up to 30W, and PoE++ (IEEE 802.3bt) can reach 90W (also called Hi-PoE). Choose the rating that meets the power needs of your devices.
Related Articles
PoE Certification: An Overview of Various Safety Standards in the PoE Industry
An overview of various safety standards in the PoE industry, highlighting the importance of PoE certification for ensuring reliable and secure network performance.
ISO Compliance: An Introduction to ISO Facility Standards and Their Impact on PoE
This article delves into ISO compliance that facilities must adhere to, ensuring quality management, environmental responsibility, and operational efficiency.
Outdoor PoE Injector: Understanding PoE Ratings For Ensuring Reliable PoE Systems
Explore essential PoE ratings to ensure reliability and efficiency in outdoor PoE injector systems.

Future PoE Trends
PoE Lighting
PoE lighting is an emerging trend that leverages Power over Ethernet technology to power and control LED lighting systems through network cables. This innovative approach offers several advantages, including simplified installation, reduced wiring costs, and enhanced energy efficiency. PoE lighting systems can be easily integrated with smart building technologies, enabling centralized control, automation, and real-time monitoring of lighting conditions. This integration allows for dynamic adjustments based on occupancy, natural light availability, and energy-saving protocols. As smart building and IoT technologies continue to advance, PoE lighting is poised to play a significant role in creating more energy-efficient and intelligent building environments.
FAQ
What applications will benefit most from the development of Over 100w PoE standards?
Over 100w PoE will enable powering high-power devices like PTZ security cameras, digital signage displays, and even some industrial automation equipment directly through Ethernet cables. This can eliminate the need for separate power supplies and further streamline installations.
How might PoE lighting contribute to the growing Internet of Things (IoT) trend?
PoE lighting fixtures with built-in sensors can collect valuable data on occupancy, ambient light levels, and even temperature. This data can be fed into IoT networks for real-time building monitoring and optimization.
Related Articles
PoE Lighting: Illuminating the Future with Emerging Trends in PoE Lighting Technology
Discover how Power over Ethernet revolutionizes indoor lighting with PoE technology, enhancing efficiency and control.
Industrial Ethernet: Streamlining Power and Data for Optimal Network Performance
Discover 2-wire PoE technology advancements streamlining power and data in industrial internet settings, enhancing reliability, and cutting costs.
How PoE Powers Smart Cities: Transforming Urban Living with Advanced Technology
Explore how Power over Ethernet (PoE) powers smart cities, enhancing urban living through advanced technology.
Conclusion and Next Steps for Businesses
To recap, we have discussed all there is to know about Power Over Ethernet products and how Phihong champions every aspect of manufacturing and design of them. It’s crucial to understand that not all manufacturers share the same commitment to your success and the satisfaction of end-users as Phihong does. If you seek a lasting partnership built on mutual success and unwavering dedication, consider Phihong as your trusted ally. Call us today if you have any questions about our products or become a partner with us, call: 510-445-0100 or email us at usasales@phihongusa.com. We look forward to talking with you.